Primary Units:
The first unit of Primary treatment is the Inlet Chamber, in which the discharge from Common
rising main through Raw Sewage Pumps is received. The inlet chamber is mainly used to
control the velocity of raw influent and also for its smooth distribution of flow to the fine screen
channel. The fine screen channel will be equipped with manual screen & mechanical screen as
required designed for peak flow velocity. Necessary hand operated sluice gate shall be provided
at upstream of the chamber to isolate the screen when it is under maintenance. The screenings is
conveyed to the disposal through a belt conveyor and further it is to be disposed off by suitable
arrangement.
The screened influent then flows to the Grit chambers where the heavy inorganic matter is
separated. The Grit free waste thus obtained will flow to SBR basin. At this stage physical
treatment of raw influent known as Primary Treatment completes.
SBR Process:
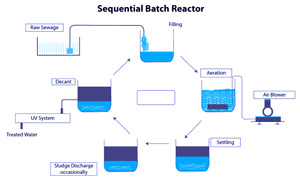
SBR is a SEQUENTIAL BATCH REACTOR process. It provides highest treatment
efficiency possible in a single step biological process.
SBR – System is operated in a batch reactor mode which eliminates all the inefficiencies of the
continuous processes. A batch reactor is a perfect reactor, which ensures 100% treatment. Two
modules are provided to ensure continuous treatment. The complete process takes place in a
single reactor, within which all biological treatment steps take place sequentially.
NO additional settling unit / secondary clarifier is required!
The complete biological operation is divided into cycles. Each cycle is of 3 – 5 hrs duration,
during which all treatment steps take place.
A Typical Cycle
During the period of a cycle, the liquid is filled in the SBR Basin up to a set operating water
level. Aeration Blowers are started for aeration of the effluent. After the aeration cycle, the
biomass settles under perfect settling conditions. Once Settled the supernatant is removed from
the top using a DECANTER. Solids are wasted from the tanks during the decanting phase.
These phases in a sequence constitute a cycle, which is then repeated.